What is Application Architecture?
Data architecture is explains and enables the data needs of the enterprise. It is described through four elements—data needs, major sources of data, major types of data, and the required data management resources.
We use four enterprise architecture models to describe your data architecture - the subject model, subject area model, logical data model, and logical document model.
Application architecture has a following role in information systems architecture. It follows data architecture. Information Systems Architecture is a special architecture domain that aligns functionality, data flow, and data management. In practice, this means ensuring that applications are delivering the required data flow and data management, not just delivering features.
Let's focus on this assertion for a moment. Applications exist to process and manage data. Without a solid understanding and design of Data Architecture, applications become disconnected islands. As they deliver features, they deliver technical debt. They create complexity in data flow and data management. Complex data flow and data management accelerate your technical debt, and add complexity to data governance.
This means your application architecture is focused on the structure and interaction of the applications that provide needed functionality and data management, you have an information systems architecture.
No successful digital transformation will be built on functionality. They are always built on data.
Four Elements of Application Architecture
Every application architecture will address:
By themselves these elements help us understand the structure of our applications - what they do, how they should be assembled, and how the parts interact.
Our applications exists to manage data and deliver functionality.
We are chasing how will we group and assemble required functionality and data management. Assembly is the critical application architecture challenge.
Keep in mind that functionality can be placed anywhere - embedded in an enterprise application, exposed by a micro-service, or hard-wired into an ASIC. Assembly is drives integration boundaries, lifecycle and dependency.
We know that application architecture enables great enterprise architecture. You must know functionality, data flow, and data management. Data flow mandates how application architecture and data architecture enable your business architecture.
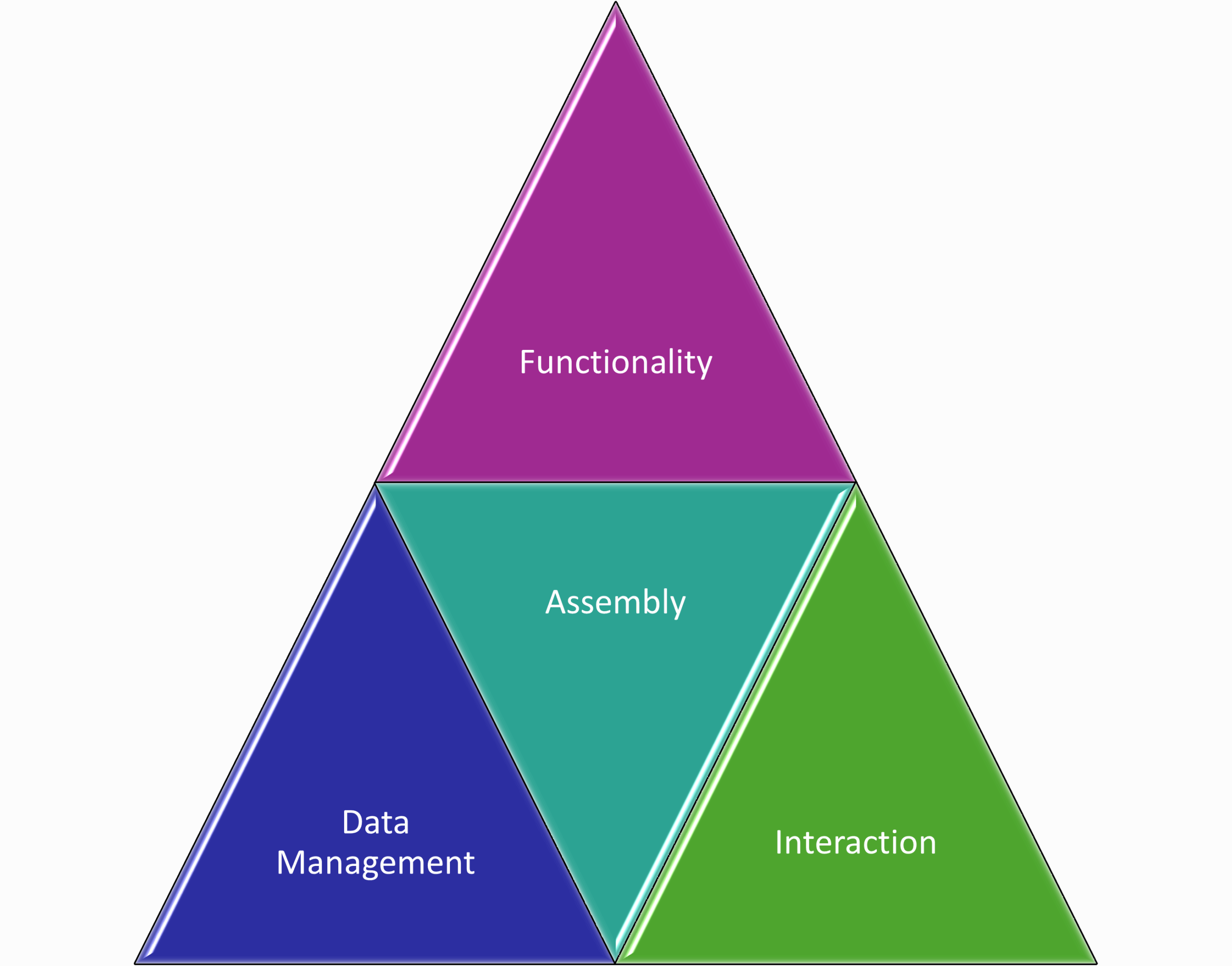
Functionality
Application architecture starts with functionality.
Functionality falls into four groups:
- Functionality needed to do the work: When the applications perform the task. This is the most interesting functionality in an automated system.
- Functionality needed to record the work: When something else performs the task, and the functionality simply records the data created or that the work happened. Most software functionality falls into this group - it records information for people, or other automated systems.
- Functionality needed to manage the work: Scheduling, task management, coordination, and all the activity tracking. This is necessary for well managed high efficiency business activity. It is often overlooked when we talk about the work.
- Functionality needed needed to manage the data: Storing, retrieving, mixing, evaluating, moving and securing the data.
You need to have a consistent set of functionality. In most of our models we distinguish recording and doing as an attribute.
When we overlook functionality to manage—either the work or the data—we diminish the value of our systems.
Functionality is directly tied to the Logical Function Model.
Assembly
Considering how best to assemble functionality is the most important job for an application architect.
Assembly is where you create or minimize integration and data flow complexity. It is where you gain re-use, specialization, and and meet unique operational requirements.
Assembly is not done from the perspective of a theoretical best. It is done with regard to hard reality and operational requirements. Consider the performance and power advantages of custom ASICS. Or, the performance and data implications of whether the function happens on a mobile device or the data center. Or, the integration challenges when you are balancing multiple commercial systems and a custom bolt-on.
Assembly is directly tied to the Logical Services Model.
Interaction
How will the different parts of your application portfolio interact.
Simple decisions about whether you use a Message Bus, API, or a shared database are choices directly tied to application agility, sustainability, and management of technical debt.
Strong application architects understand why functionality is assembled and the methods of interaction between the different assemblies.
Interaction is directly tied to both the Logical Service Model and the Logical Integration Model.
Data Management
Tools and systems that deliver the needed data where, when, how, with the right quality, confidence and security.
Like interaction simple decisions will drive data quality, security, risk and sustainability.
Navigate Application Architecture Model Kinds
Navigate provides an end-to-end architecture model. We create this end-to-end model through discrete model kinds. A model kind can support specific analysis, or focus on a separate aspect of the end-to-end model. In simple terms, a model kind is a specific type of modelling.
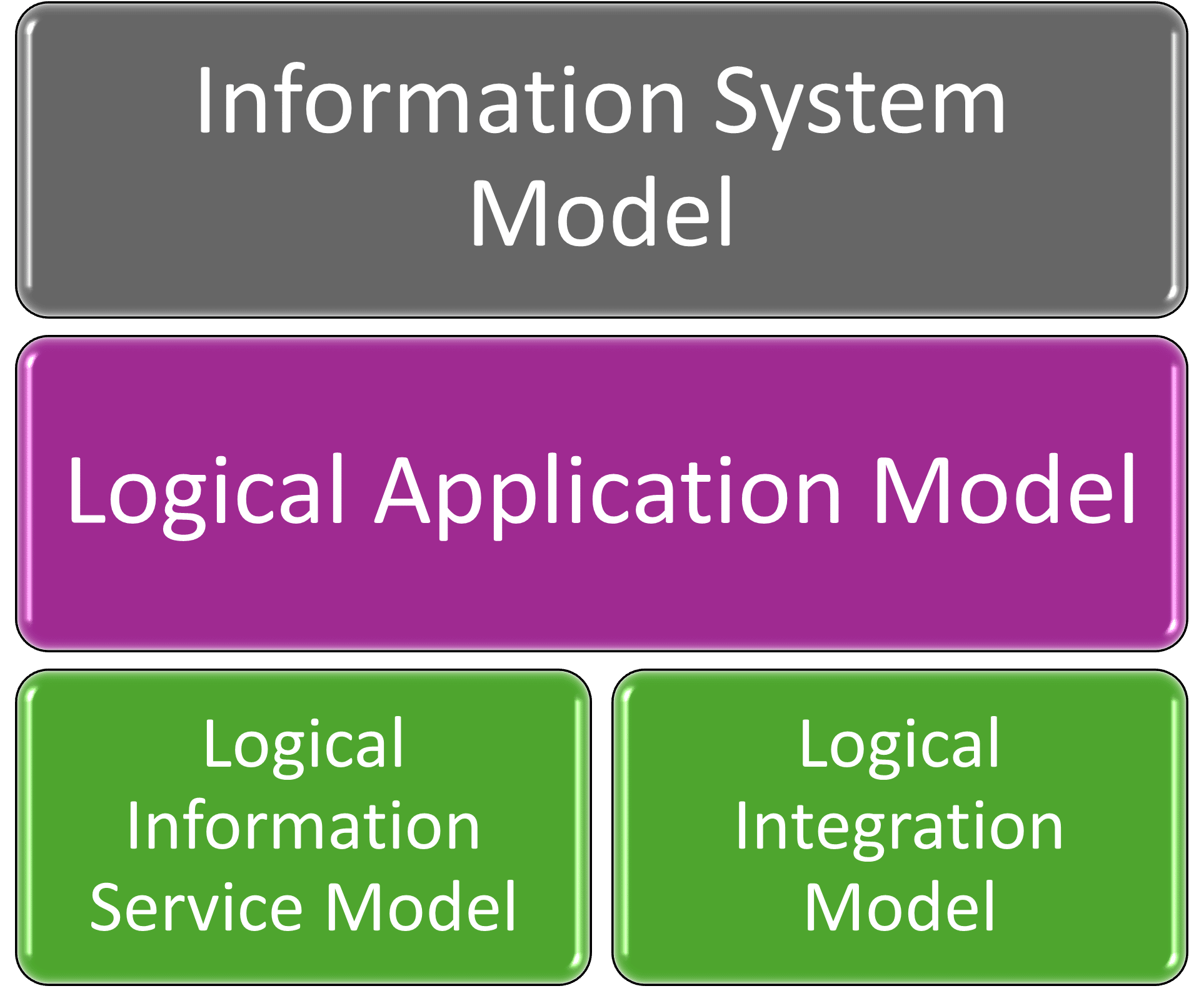
We build around four regular application architecture model kinds:
- Information System Model
- Logical Application Model
- Logical Information Service Model
- Logical Integration Model
These specialized models combine to develop the EA Landscape following the best practice of incrementally extending it one architecture project at at time.
Using model kinds drive consistency and re-usability driving productivity and consistency across an EA Team.
Navigate Model Kind Description
Each model kind is defined by:
- Purpose: Why this model kind exists and what questions it's intended to answer.
- Scope: Outlining the boundaries of what’s included and excluded within the model kind.
- Content & Structure: The components, relationships, and properties that should be used when creating instances of a model kind.
- Modelling Approach: Guidance on how what is included or excluded to focus on specific aspects relevant to the objectives.
- (Optional) Relationship with other Model Kinds: Describes the purpose of the link and what relationship is used to bridge the two models.
Information System Model
Information System Model Scope
Provides holistic representation of the automated systems landscape, illustrating core Information Systems (like CRM or SCADA system).
We use automated systems deliberately. Self-driving trucks, IoT, and applications are all automated systems
A strong Information Systems Model provides a shared understanding of the application landscape. It frames conversations through a common understanding. Use this model to provide broad direction to the Information System Portfolio
Information System Model Guidance
Enterprise-wide
- 10-20 Major Systems
Department-wide Architecture project
- Expect 5-10 Major Systems
Transformation Initiative
- Expect 5-15 Major Systems
Information Systems Properties
-
-
How will we approach buying or building (Commercial Suite, Commercial B-o-B, Opensource Suite, Opensource B-o-B, Custom Evolution, Custom Cloud-Ready, Custom, Saa)
-
Agility
-
-
How much unexpected change pressure? Unexpected change pressure comes from threats and opportunities. It is highest in systems directly tied to the value proposition, products, and services.
-
Resiliency
-
-
How much resiliency is required?
-
Duplication
-
-
Do we want duplication? Will we accept duplication? Or will we pay extra to prevent duplication?
-
Standardization
-
- Will we pay extra to require Standardization? Will we accept variation? Or will we demand specialization?
Hosting
Logical Application Model
We model functionality falls into three groups:
- Functionality needed to do or record the work
- Functionality needed to manage the work
- Functionality needed needed to manage the data
Logical Application Model Guidance
We use a simple taxonomy of 2-3 levels.
5-10 Logical Applications across an Information System
Each of these level 1 Logical Applications is decomposed into 3-5
Aim for a sweet spot of ~20-25 Logical Applications. You must keep the model manageable.
Less than 25% will be architecturally interesting
The other 75% provide completeness and coverage
Logical Application Properties
Agility
-
- How adaptable to unexpected threats & opportunities
Development Priority
-
- Depth of Feature, TTM, or Sustainability
Resiliency
-
- Does the System need to absorb failures and keep running
Lifespan
-
- What is the needed lifespan
Standardization
-
- Do we need standardization? Should we seek overlap?
Offline Support
-
- Does it need to run someplace? Laptop, mobile, on a submarine
Logical Service Model
We call this a Service Model, for historic reasons - Service-Oriented Architecture language has caused us to re-think. All we are talking about is a 'black box' that delivers a set of functionality and can be assembled with other 'black boxes'.
The Logical Service Model:
- Defines Boundaries
- Clarifies Integration Points
- Enables Consumer-Centric Assembly
- Drives Contract Terms
What are the terms of change, restrictions on use and access
Logical Data Model Guidance
Creating bundles of functionality to drive implementation.
Inside the assembly there are:
- Consistent contract terms
- Consistent approach to deliver
- A data management boundary
- An integration boundary
Logical Service Properties
Agility
-
- How adaptable to unexpected threats & opportunities
Duplication
-
- Diversified, Replicated, Shared
Development/ Procurement
-
- What is the right acquisition path
Development Priority
-
- Depth of Feature, TTM, or Sustainability
Resiliency
-
- Does the System need to absorb failures and keep running
Lifespan
-
- What is the needed lifespan
Standardization
-
- Do we need standardization? Should we seek overlap?
Offline Support
-
- Does it need to run someplace? Laptop, mobile, on a submarine?
Logical Integration Model
The Logical Integration Model explains what happens between Information Systems or Logical Services.
It addresses all important boundaries. Not just automated information flows.
Used to
- Define Integration patterns & reference Architectures
- Expose Data Transformation
- Enforce Data Requirements (Security, Lineage, Source)
Logical Integration Model Guidance
We either build a formal logical integration model defining the interfaces and the 'broker in the middle, or use a simple statement of an architecture pattern. The formal model will explain a one-of or be used as a reference architecture and the basis of the integration patterns.
Logical Integration Properties
Agility
-
- How adaptable to unexpected threats & opportunities
Duplication
-
- Diversified, Replicated, Shared
Provider
-
- Internal, External
Resiliency
-
- Does the System need to absorb failures and keep running
Lifespan
-
- What is the needed lifespan
Standardization
-
- Do we need standardization? Should we seek overlap?
Technical Fit
-
- Does this integration need to comply with special technical requirements?
Everything Revolves Around Data Needs
Yes, your application architecture revolves around data needs— the applications exist to process and manage data.
Without data we do not need software.
Your business activity created, mixes, and consumes data. Data used to manage the process. Data used to record the activity. Or data central to the business activity.
In the application and business activity you need to match
- source and need
Source and need define flow, which drives data management - data management
Quality, flow, and security define the data management resources required
Remember:
Data needs drive a path through fractured application landscapes
Data needs break silos
Data needs drive real data flows
Conclusion of What is Application Architecture?
Application architecture is a key contributor to the information systems architecture. Information Systems Architecture is the architecture domain that aligns data management, functionality, and data.
Application architecture uses four elements—functionality, assembly, interaction, and data management.
Four enterprise architecture models describe your application architecture:
- Information System Model
- Logical Application Model
- Logical Information Service Model
- Logical Integration Model
Common practice focuses on functionality and integration without understanding data needs, data flow, and required data management. This inevitably creates complexity and technical debt.
Best practice leads with data, and ensures the application architecture is focused on the structure and interaction of the applications that ... manage the data assets.
We know that application architecture enables great enterprise architecture. Functionality, data flow, and data management enable your business architecture.
No successful digital transformation will be built on functionality. They are always built on data.