What is Data Architecture?
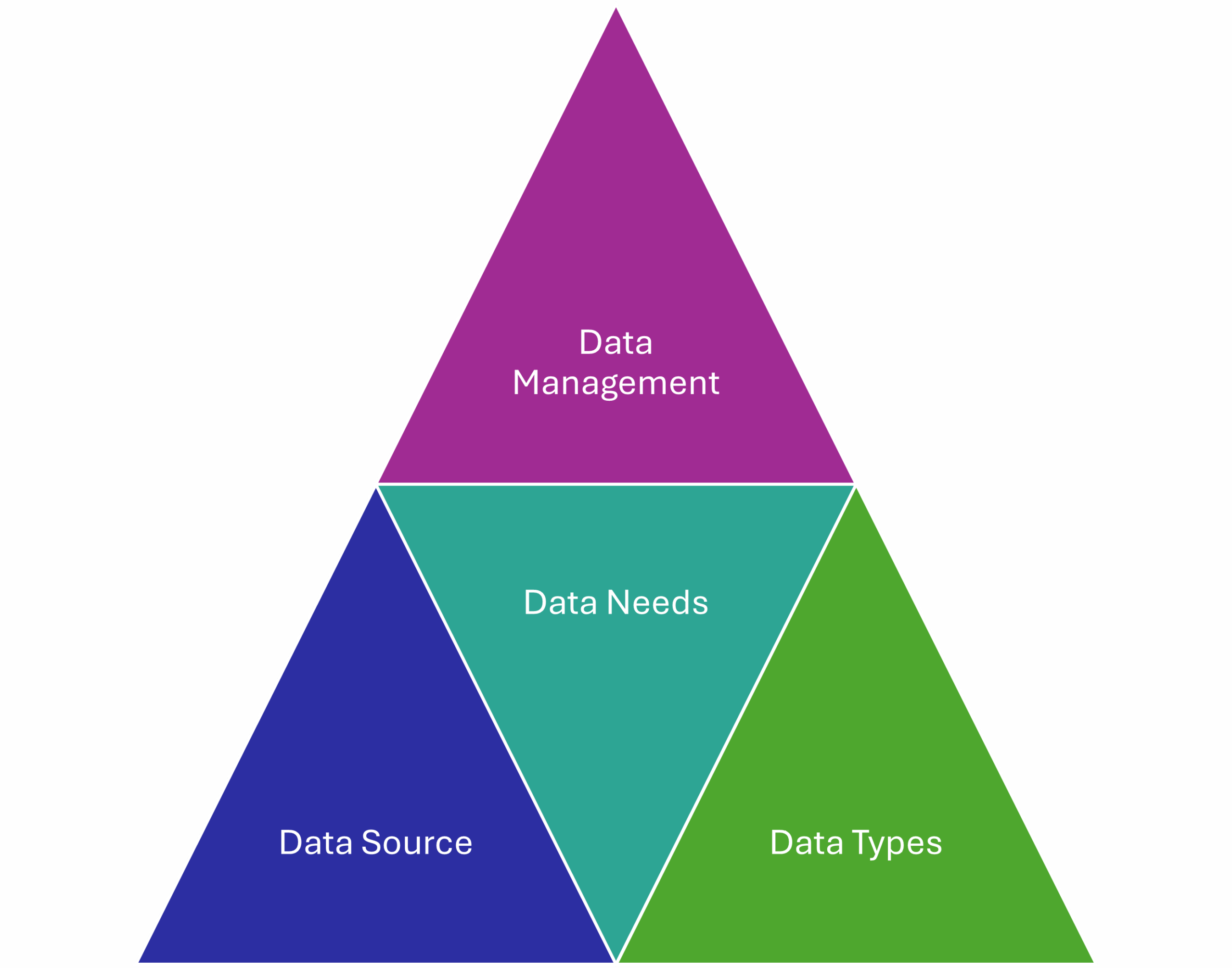
Data architecture is explains and enables the data needs of the enterprise. It is described through four elements—data needs, major sources of data, major types of data, and the required data management resources.
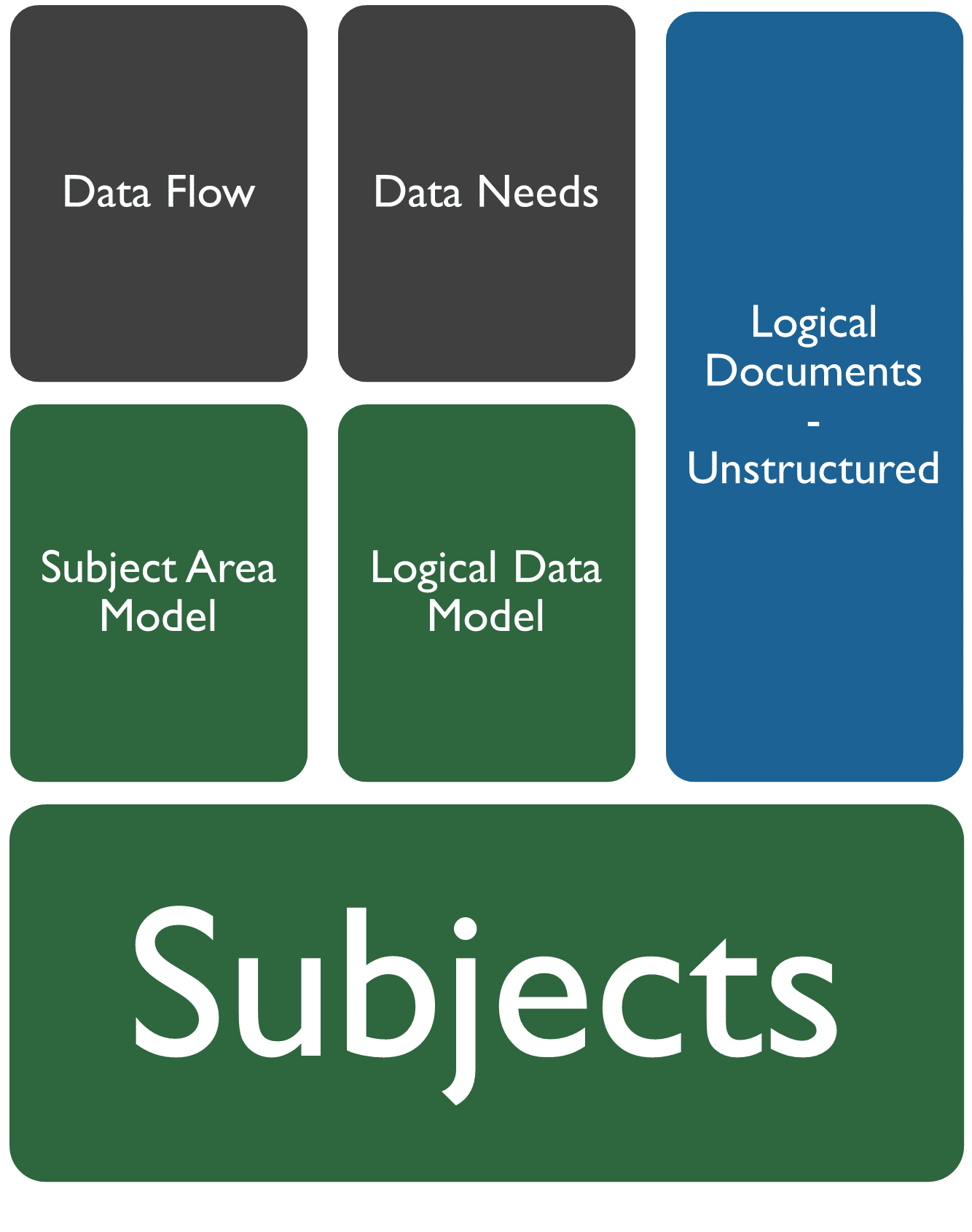
We use four enterprise architecture models to describe your data architecture - the subject model, subject area model, logical data model, and logical document model.
Data architecture is the leading part of the information systems architecture. The Information Systems Architecture is a unique architecture domain that aligns functionality, data, and data management. In practice, this means ensuring that applications are delivering the required data flow and data management, not just delivering features.
Common practice pushes data architecture to the background. We obsess about features and talk about applications — what they do, how they’re built, or how they integrate with other systems.
Applications exist to process and manage data. Without a solid understanding and design of Data Architecture, applications become disconnected islands. As they deliver features, they deliver technical debt. They create complexity in data flow and data management. Complex data flow and data management accelerate your technical debt, and add complexity to data governance.
When you lead with data , and ensure the application architecture is focused on the structure and interaction of the applications that ... manage the data assets, you have an information systems architecture.
No successful digital transformation will be built on functionality. They are always built on data.
Four Elements of Data Architecture
Every data architecture will address:
By themselves these elements help us understand the structure of the data.
We are chasing an understanding of data flow. Data flow is explained by data sources and data needs are the bookends of data flow—where it comes from, and where it is needed.
Keep in mind that once data starts moving it can go anywhere. Flow requires controls; it requires data management resources.
We know that data architecture steers great enterprise architecture. It can only steer if you know the data flow. Required data flow mandates how application architecture and infrastructure architecture enable your business architecture.
Data Needs
Everything starts with the data needs of the enterprise.
Data needs fall into three categories:
- Data needed to create products and services: Information your products and services depend on.
- Data needed to operate the business: Transactional, operational, and process data that keep day-to-day activities running smoothly.
- Data needed to maintain records: Contractual and regulatory defined information necessary for compliance.
Do not get confused about data needs — you must ruthlessly separate what’s nice to have from what’s needed.
Needed does not require modifiers like absolutely, or important. Needed is simply necessary.
Major Sources of Data
Where data is created, or collected, and where it is transformed. Data comes from manual processes, applications, devices, and external partners. Understanding the source system is central to data quality, lineage and governance.
Major Types of Data
Identifying key data categories relevant to your business—customer, product, financial, operational, and so forth. This classification helps focus architectural efforts and governance.
Usually the major types of data are defined in the Subject Model
Data Management Resources
Tools and systems that deliver the needed data where, when, how, with the right quality, confidence and security. In practice these are a broad set of requirements directed at the application and infrastructure architectures.
Navigate Data Architecture Model Kinds
Navigate provides an end-to-end enterprise architecture landscape. This is a specific way of saying we work towards an end-to-end model architecture model.
We develop the EA Landscape following the best practice of incrementally extending it one architecture project at at time.
We manage the enterprise model through discrete model kinds. A model kind can support specific analysis, or focus on a separate aspect of the end-to-end model. In simple terms, a model kind refers to the conventions for a specific type of modelling.
Each model kind is optimized to tell us something about the architecture.
Different model kinds will explore:
- motivation and strategy
- parts of an architecture domain
Using model kinds drive consistency and re-usability driving productivity and consistency across an EA Team.
Navigate Model Kind Description
Each model kind is defined by:
- Purpose: Why this model kind exists and what questions it's intended to answer.
- Scope: Outlining the boundaries of what’s included and excluded within the model kind.
- Content & Structure: The components, relationships, and properties that should be used when creating instances of a model kind.
- Modelling Approach: Guidance on how what is included or excluded to focus on specific aspects relevant to the objectives.
- (Optional) Relationship with other Model Kinds: Describes the purpose of the link and what relationship is used to bridge the two models.
Enterprise Data Model Notes
We draw Navigate's data model kinds from DAMA's The Enterprise Data Model. The Enterprise Data Model is comprised of the Subject Model, Subject Area Model (SAM), and Logical Data Model (LDM). Both the SAM and LDM are built from the Subjects. They serve distinct, but interconnected, purposes.
The Subject Model describes the organization's data landscape. Every Subject is meaningful to the data landscape.
The Subject Area Model is business-centric view. It’s about understanding a specific business domain - a "Subject" - in detail. The SAM defines Subject in a way that’s readily understandable by business stakeholders. It’s a narrative of the data, focusing on what it means.
The Logical Data Model, is a technically-oriented. It builds upon the SAM, transitioning from the SAM's business concepts into sufficient detail to guide implementation.
Together the SAM and the LDM speak to two distinct audiences. The SAM reflects the business understanding of the data's meaning. The LDM is guidance and constraint for the implementation. This frame is often documented in a Master Data Blueprint.
The SAM and LDM reflect the same Subject, speaking to different audiences.
Subject Model
Subject Model Scope
Subject model identifies business relevant information areas
Each Subject identifies the information needed in an area of activity or a distinct aspect of operations
Provide a shared understanding of the data landscape
Used to
- Frame discussions about the data landscape
- Highlight areas of data complexity
- Direct further modelling
Subject Model Guidance
Enterprise-wide
- 12-20 Subjects
Department-wide Architecture project
- Expect 3-5 Subjects
Transformation Initiative
- Expect 5-10 Subjects
Subject Area Model
The Subject Area Model Kind (SAM) represents the information within a single Subject. The SAM is used to ensure a common understanding of the understanding of the data landscape.
The purpose is clear - develop an understanding of the data landscape.
DAMA tells us to think about the entities that define the information in a Subject. Entities have relationships with other entities. Relationships within the Subject, and with entities in other Subjects.
Entity is just a data-way of saying a topic of information, a noun. We use the component Business Term.
Subject Area Model Guidance
The Subject Area Model uses 8-15 Business Terms (Entities) to define the Subject. Expect 1-2 Business Terms from from another subject, to complete the understanding of the Subject.
Aim for a sweet spot of ~13 Business Terms. You must keep the model manageable.
As you approach 12 Business Terms consider whether you have more than one subject
Less than 8 Business Terms suggest this might not be a deep, or important Subject.
Logical Data Model
The Logical Data Model Kind Kind (LDM) represents the information within a single Subject with the intention of guiding and constraining implementation. The LDM is used to ensure a consistent technical handling of the data landscape.
The purpose is clear - guiding implementation to ensure the data landscape enables the business' data needs.
Logical Data Model Guidance
The Logical Data Model uses 12-20 Logical Data Components (Entities). Expect 3-5 Logical Data Components from from another subject.
The LDM must include cardinal relationships, properties, and data access and data management architecture specifications
Logical Data Properties
Data Access
-
- Does this Entity have specific access constraints
Data Classification
-
- What class of data is it? (Master, Reference, Transactional)
Data Retention
-
- Does it have special retention requirements? Where do these requirements come from?
Data Type
-
- What type of data is it? (Number, text, boolean, calculated)
Data Protection Property (Optional)
-
- Does the data have unexpected protection requirements?
Logical Document Model
The Logical Document Model Kind exists to represent artifacts—such as forms, letters, or reports—relevant to a specific business activity (e.g., Quotation, Sales Order, Invoice, Bill of Lading, Job Application).
It provides context for data, facilitating understanding of data security, retention, flow, and governance. For example, data entities such as price do not convey retention or security requirements, whereas documents like the Quotation, Sales Order, and Invoice provide that context.
Logical documents cover three document types:
- Record: Documents mandated by law or contract, with externally defined content and retention requirements.
- Business Document: Documents internally defined to support business processes, governed by organizational policies for consistency and auditability.
- Transitory Document: Informal documents created and used by individuals or teams, with retention managed by internal policies and aligned to creator needs.
Logical Document Model Guidance
The Logical Document Model is easiest when an end-to-end business process is considered. End-to-end processes will use 3-10 Logical Documents.
Aim for a sweet spot of ~6 Logical Documents. You are looking for a complete list of Records, and a useful list of Business Documents and Transitory Documents to capture retention, security and quality.
Each Logical Document will contain 5-10 Business Terms or Logical Data Components.
Logical Document Properties
Document Type
-
- Record, Business Document, Transitory
Data Access Property
-
- Country-only, Organization Only, Department Only, Process Only, or Custodial Data
Data Retention Property (Optional)
-
- Ad Hoc, Departmental, Enterprise, Contract, Regulated, or Prohibited
Data Protection Property (Optional)
-
- - Relaxed, Standard, Enhanced
Everything Revolves Around Data Needs
Let's clarify about data needs— you must ruthlessly separate what’s nice to have from what’s needed.
Needed data does not require modifiers like absolutely needed, or important data. Needed is simply necessary.
The clear distinction between needed and everything else is the foundation for effective application requirements.
Once you know that a business activity needs some data everything else emerges:
- source
- flow
Needed data defines where the flow must get to. - quality
Needed data defines quality. - security
Security doesn't define where data can go. Needed data goes where it is needed. Needed data defines where the data must be securely delivered, and where it must be secured. - data management
Need + quality + flow + security define the data management resources required
Source is a challenge— especially when the provider and consumer are in different organizations or authority, or governance domains. We often imagine that data consumers define quality. They don't. Data producers define quality.
Consumers can request higher quality, but they may be faced with three choices:
- pay more
- do without
- improve the quality themselves
This is no different than any other producer/consumer relationship.
Remember:
Data needs drive a path through fractured data landscapes.
Data needs break silos.
Data needs drive real data definitions
Data needs deliver data governance.
Conclusion of What is Data Architecture?
Data architecture leads information systems architecture. Information Systems Architecture is the architecture domain that aligns data, data management, and functionality.
Data architecture is explains and enables the data needs of the enterprise through four elements—data needs, major sources of data, major types of data, and the required data management resources.
Four enterprise architecture models describe your data architecture: the subject model, subject area model, logical data model, and logical document model.
Common practice pushes data architecture to the background, and puts the spotlight on applications — what they do, how they’re built, or how they integrate with other systems.
Best practice leads with data, and ensures the application architecture is focused on the structure and interaction of the applications that ... manage the data assets.
No successful digital transformation will be built on functionality. They are always built on data.