What is Enterprise Architecture
What is Enterprise Architecture?
- Navigate Definition of Enterprise Architecture
- Gartner Definition of Enterprise Architecture
- DODAF Definition of Enterprise Architecture
Using Enterprise Architecture to Guide Effective Change

What is Enterprise Architecture?
What is enterprise architecture? The answer depends on why, what and how.
Enterprise architecture is a discipline that guides effective change
Enterprise architecture is a profession that uses models and views to explain how an enterprise works and how it can be improved
Enterprise architecture is a documented by a set of of models and views and architecture specifications
Enterprise architecture is a strategic tool that helps identify and address the gaps between our objectives and the reality of our current situation.
The purpose of enterprise architecture to guide effective change.
Enterprise architects create an architecture as a conceptual blueprint for enterprise analysis, planning, design, and implementation, The architecture is used to achieve profitable growth and strategy execution.
Navigate Definition of Enterprise Architecture
Enterprise architecture documents the preferred future state of the organization. It identifies the changes necessary to reach that state.
Enterprise architects develop the enterprise architecture
-
- by simplifying complexity to understand the enterprise finding sources of performance shortfalls how to correct them
- to advise stakeholders and sponsors about potential improvements in terms of priority, concerns, effort and risk
- ensuring that the documents highlight approved improvements and any constraints on how the improvements will be implemented
- Conexiam Navigate
In practice an Enterprise Architecture team made up of architecture domain specialists work with an Architecture Review Board. They use an architecture development method and architecture governance to find the best path forward for their organization. Their efforts are concentrated on the most valuable enterprise architecture use cases.
Gartner's what enterprise architect's do definition of enterprise architecture
“the process of translating business vision and strategy into effective enterprise change by creating, communicating, and improving the key principles and models that describe the enterprise’s future state and enable its evolution”
- Gartner
DODAF's what is an enterprise architecture definition of enterprise architecture
“a set of abstractions and models that simplify and communicate complex structures, processes, rules, and constraints to improve understanding, implementation, forecasting, and resourcing”
- DODAF
Using Enterprise Architecture to Guide Effective Change
You use an enterprise architecture to find the best available end-to-end alignment of ends and means. Where your organization wants to arrive are the ends. Usually described as a goal, objective or performance expectation. Means, these are how the changes happen. They might be a strategy, a program, a project or a digital product.
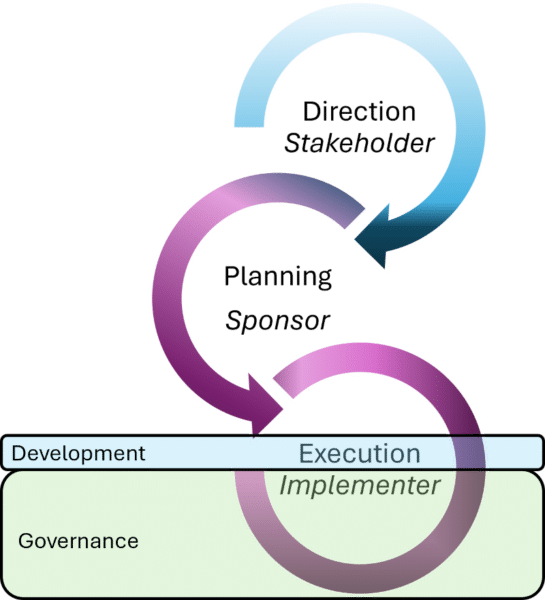
The diagrams below show the cascade of decision making. It is based on providing direction - sending performance expectations, constraints and risk appetite down the organizational structure. Enterprise architecture helps translate the direction, often through refining constraints to the next decision.
To explain direction in enterprise architecture consulting we use a simple example: the CEO is told to grow revenue through new products to existing customers.
As architects we use the set of architecture constraints - work packages, principles, patterns, and the target state to guide and constrained choices down the chain of decisions.
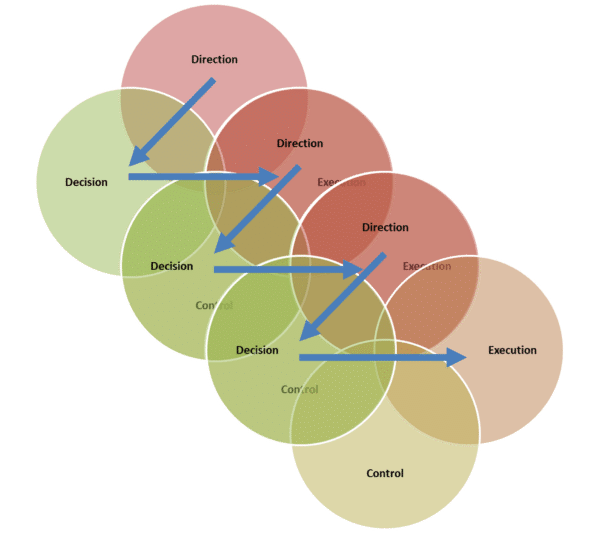

An architected approach provides a standard method and language to guide effective change from the top to the bottom of your organization.
Classic enterprise architecture use cases show how the same essential scaffolding are adapted as the decision and action moves down your organization.

Enterprise Architecture Use Cases
The use cases are focused on consistent points where significant decisions about how to address a shortfall are made. There are four classic EA Use Cases:
- architecture supporting strategy
- architecture supporting portfolio
- architecture supporting project
- architecture supporting solution delivery
Enterprise Architecture to support Strategy Use Case
Enterprise architecture to support strategy is used to identify change initiatives and supporting portfolio and programs.
It sets the terms of reference, identifies synergies, and governs the execution of strategy via portfolio.
Strategy will address:
- Enterprise Strategy
- Department Strategy
- Initiative Strategy
It requires a Target Architecture to:
- define Portfolio
- govern activity
Improved by a Roadmap
- Transition stages & decision points
Architecture work:
- is improved by scenario analysis
- needs an end-to-end view
- creates boundaries and outcomes of change initiatives & portfolio
- identifies synergy & dependency
- creates strategy, work package, principle and patterns
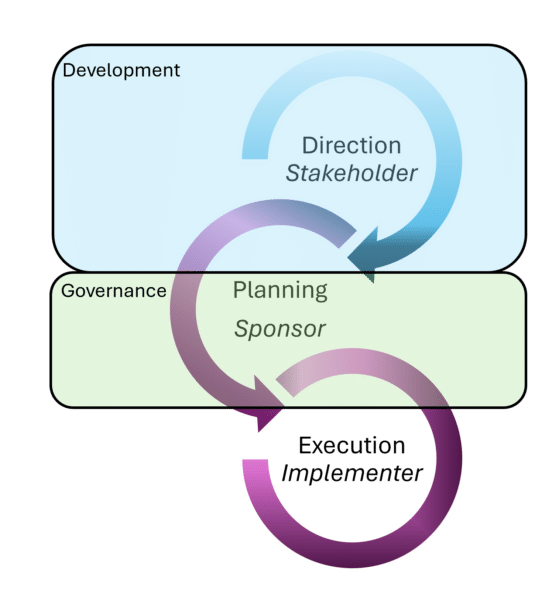
Enterprise Architecture to support Portfolio Use Case
Enterprise architecture to support portfolio is used to identify projects with a change initiative or portfolio. It is based on an existing portfolio that has a defined outcome and set of constraints.
This architecture set a project's terms of reference, aligns project approaches and identifies synergies. A key use is governing execution.
The architecture addresses an existing portfolio.
It requires an architecture roadmap to:
- select activity to reach transition ststes
- define transition stages & decision points
- govern activity (Direction & Control)
It is usually tightly aligned with the budget cycle.
Architecture work:
- is improved by reference architectures
- needs an end-to-end view
- will break the end-to-end view into systems of interest
- identifies projects
- define project terms of reference
- align project approaches, synergy, and dependency
- creates target architectures, work packages, principles, patterns, and standards
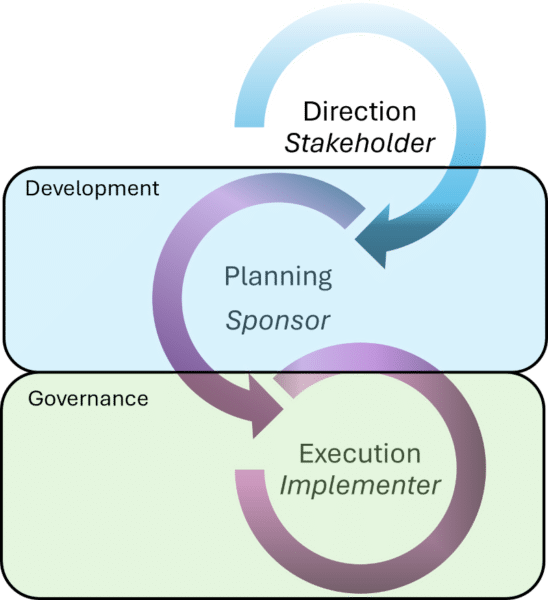
Enterprise Architecture to support Project Use Case
Enterprise architect's that support project are directly assisting their organization's project delivery method. Their involvement is primarily transferring direction from the enterprise architecture to the project. They enable implementation governance and alignment between projects.
The project needs terms of reference (Boundary, Approach, OKR, Constraints, Work Packages, Gaps).
Architecture work:
- is improved by an architecture roadmap and transition architecture
- depends upon reference architectures
- should have an Implementation Plan
- is focused on a few Systems of Interest that the project will modify
- is heavily constrained by superior architecture specifications (Work Package Strategy, principle, pattern, control, and standard)
Is aligned with project initiation and the budget cycle.
Delivers value through:
- strategy & portfolio governance
- clarifying the purpose and value of the project
- aligning projects through dependency, integration, and synergy
- provides direction (performance expectation, constraints, risk approach and implementation strategy to the project designers
- directing procurement and contracting
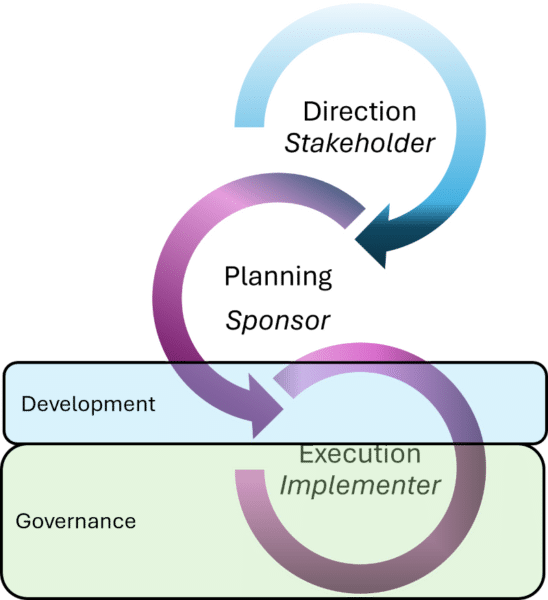
Enterprise Architecture to support Solution Delivery Use Case
Enterprise architect's that support solution delivery are engaged in their organization's project delivery. Their involvement is primarily transferring direction from the portfolio-oriented architecture to the solution delivery. They enable implementation governance.
The Solution needs terms of reference (Boundary, Approach, OKR, Constraints, Work Packages, Gaps). This can be delivered through a TOGAF architecture contract.
Needs an superior architecture that provides:
- the boundary of the solution and the gaps that are being filled
- constraints from transition architecture and an end-to-end view
- Superior Architecture Specifications
Architecture work:
- is focused on a Systems of Interest that the project will modify
- is heavily constrained by superior architecture specifications (Work Package Strategy, principle, pattern, control, and standard)
- is improved by a transition architecture
- depends upon reference architectures
- should have an Implementation Plan and implementation strategy
Is aligned with project initiation.
Delivers value through:
- strategy & portfolio governance
- fitting the solution into surrounding portfolio and project contexts to create align dependency, integration, and synergy
- providing direction (performance expectation, constraints, risk approach and implementation strategy to the implementers
- directing procurement and contracting
What does an Enterprise Architecture Look Like?
Documents. We often refer to the enterprise architecture as the binder. This analogy came from the concept of an architecture definition document. We though of different section to address architecture domains, stakeholder views, transition architectures, etc.
The Practitioner's Guide tells us that an enterprise architecture is documented by:
- Architecture Models
- Views
- Other useful things
Your customized enterprise architecture framework will be aligned with your EA use case. It will provide:
- Analytic Models
- Viewpoint Library
- Taxonomy
- Reference Architectures
- Form of Architecture Specifications
- Deliverables
In practice the architect will use the models, views, and reference architectures. Everyone else will consume the other useful things - architecture specifications and deliverables.
The concept of the architecture landscape helps put a few of these concepts together.
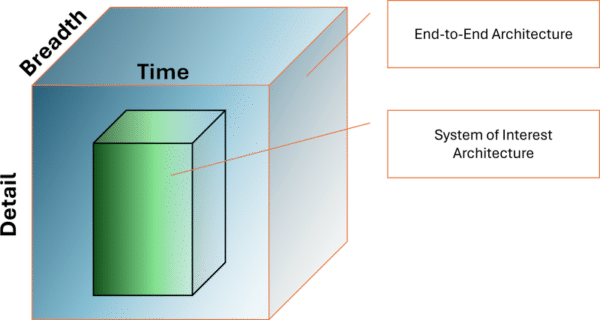
In the diagram above, the complete architecture is defined in terms of breadth, planning horizon and level of detail. The TOGAF architecture development method guides us to fill in the landscape one architecture project at a time.
The section above tells us we will build enough architecture to select portfolios, define projects, and scope solutions. in formal modelling terms each of these is a system of interest, a thing to be modelled.
To develop an enterprise architecture you will need one or analytic models and descriptive models. These models will cover every domain:
- Business Architecture Models
- Application Architecture Models
- Information Architecture Models
- Data Architecture Models
- Technology Architecture Models
- Security Architecture Models
Most of the analytic models are specialized models.
Views are used to analyze the architecture in terms of a stakeholder concern. A concern will be something like Agility, Change Impact, or Alignment.
As an architect we will have models that explain how our organization works. Our stakeholder will have given us a problem, and we will analyze potential solutions in terms of concerns.
Lots of information. Very little of it of interest to anyone else.
We use formal models in an enterprise architecture management tool, like Avolution ABACUS.
Key Enterprise Architecture Deliverables
Everyone else want to know what to do to reach the target.
We will provide:
- strategy
- architecture roadmaps
- work packages
- architecture specifications
- architecture contracts
In Navigate we have a set of templates we use to communicate about the architecture:
- problem statement
- option analysis
- project terms of reference
- uncertainty analysis
- implementation assessment
- get-well recommendation
- architecture decision record
Why Enterprise Architecture?
The reason is simple. Enterprise architecture helps make hard decisions. Complex challenges without clear answers. Enterprise architecture answers questions like:
- Whether to change?
- What to change?
- How to change?
- What to leave alone?
- How to deal with failing change?
Enterprise architects develop enterprise architecture to advise stakeholders. Then use the architecture's specifications to guide and constrain implementers.
Use enterprise architecture when you have a wicked problem. A problem with competing criteria. Competing criteria, like cost, speed, agility, time-to-market, security, sustainability.
Anyone can design to support one outcome. One outcome is easy, throw away every other criteria. Balancing multiple criteria is difficult. Especially when you adjust for benefits, effort and risk.
The Business Leader's Guide to AI has a great section on evaluating potential changes in terms of benefit, effort and uncertainty.
Tests for a Wicked Problem
- The problem is not understood until after the formulation of a solution
- No stopping rule
- Solutions are not right or wrong
- Essentially novel and unique
- Every solution is a 'one shot operation’
- No given alternative solutions
What is the Value of Enterprise Architecture?
In short, enterprise architecture is understanding the real-world in a way that allows deliberate change.
Value of Enterprise architecture
- better decisions
- aligned decisions and actions
- accountable decisions and actions
The value of enterprise architecture is that it increases the chance of successful change.
What is Useful Enterprise Architecture
Unfortunately, you cannot look at most enterprise architects and EA Teams and see what they do. Therefore, we have the recurrent question.
Sadly, most people with the job title Enterprise Architect are not doing enterprise architecture. Most of what they do is not recognizable as enterprise architecture.
An enterprise architecture is a simplification of complex reality. Useful enterprise architecture has several characteristics.
- it explains how a deficiency in our organization exists
- it provides a way of assessing change against multiple criteria
- it directs change to improve and organization
For stakeholders, performing trade-off to reach an architectural decision, engaging in scenario analysis, or examining a view is informative. They understand the impact of different options. The potential benefit, the work and where there is uncertainty.
The core value of enterprise architecture is informed decision-making.
Successful Enterprise Architecture Case Studies
Successful Enterprise Architecture makes a difference. They use the same framework and the same method and make exponential changes.
Conclusion
We started with a question. What is enterprise architecture? The answer depends on why, what and how.
Enterprise architecture is a discipline that guides effective change
Enterprise architecture is a profession that uses models and views to explain how an enterprise works and how it can be improved
Enterprise architecture is a documented by a set of of models and views and architecture specifications
The value of enterprise architecture is improved decision making and controlled implementation.
We encourage you to develop your enterprise architecture team, and professional development. Leading enterprise architecture is a thing of beauty. Leading enterprise architecture is invaluable.
Conexiam Enterprise Architecture Consulting are specialists with experience in multiple industry verticals across the US, Canada, Africa and the Middle East.
We do two things
Our approach to developing architecture that guides effective change and developing EA teams is the industry standard practice.